Nervous Energy Advanced Experiment
Background
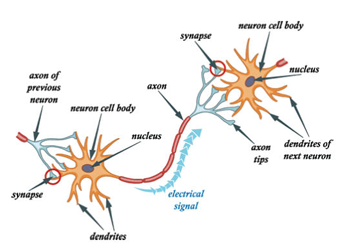
| Nerve impulses travel from one
neuron (nerve cell) to another in
the form of electrical signals. Each
neuron consists of a cell body,
short threadlike projections called
dendrites, and one longer thread
called an axon. The electrical
signals are received by the
dendrites of a neuron and then
passed along the axon to the
dendrites of adjacent neurons. |
 |
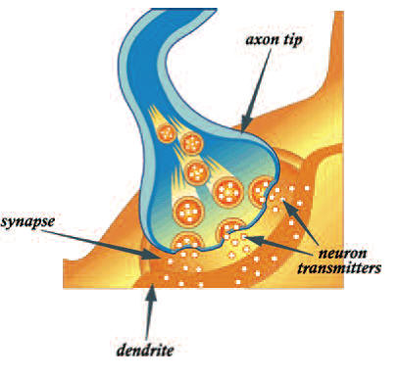
| Interestingly, axons and dendrites
don't actually touch. There is a
space between them, called a
synapse. So how does the electrical signal
"jump" the gap? You could say the energy
changes form. The electrical current causes
chemicals in the axon tip to be released. These
chemicals, called neurotransmitters, flow
across the synapse and lock on to the dendrite
of the next neuron, where they cause new electrical
signals to be generated and passed on in
the same manner. You can use common electronic components to model how nerve impulses get relayed from one neuron to another in the body. |
 |
Materials
- 6-volt battery
- 2 battery holders
- 3-volt DC buzzer
- 1 infrared phototransistor
- 1 jumbo super-bright LED (light-emitting diode)
- electrical tape
Steps
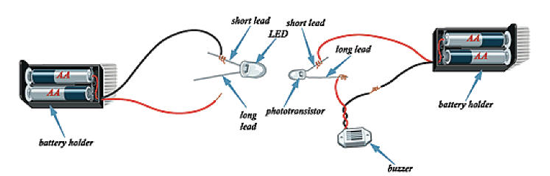
1. Set up the equipment as shown. Make sure the shorter lead of the LED is connected to the black wire of the battery holder. Similarly, make sure the shorter lead of the phototransistor is connected to the red wire of the other battery holder. Wrap a small piece of electrical tape around each connection.
2. You should have two circuits. The circuit on the left contains batteries, wire, and an LED. The circuit on the right contains batteries, wire, a phototransistor, and a buzzer. Electricity travels in a loop called a circuit. Every circuit has an energy source, wires, a load, and a switch.
3. Line up the LED with the phototransistor, leaving about a half-inch of space between them. Then touch the end of the loose red wire to the long lead of the LED. The LED should light up and the buzzer should sound. If the buzzer doesn't sound, check the alignment of the LED and the phototransistor and then repeat until it does.
Questions
Congratulations. You've just modeled how nerve impulses get transmitted from one neuron to the next. Now test your understanding by answering the following questions.
1. Which part of the setup represents:
neuron cell bodies?__________________________ an axon?________________________________
the axon tip?________________________________ the synapse?____________________________
a dendrite?__________________________________ the nerve impulse?______________________
2. How is the light from the LED like the neurotransmitters released by an axon tip?
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
3. Why do you think the buzzer was used in this demonstration?
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
4. What might the buzzer represent in the body?
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
